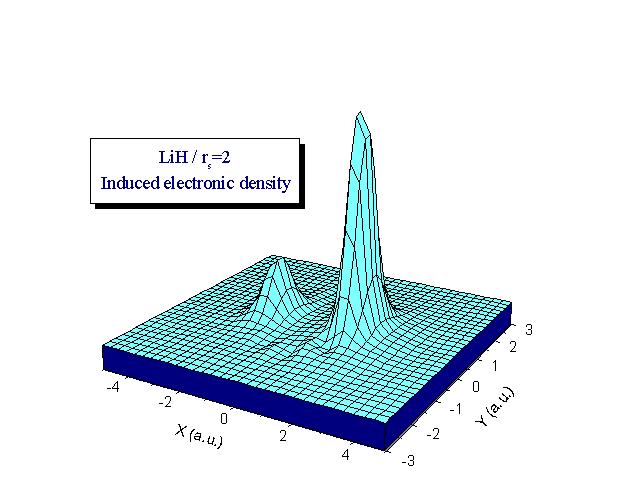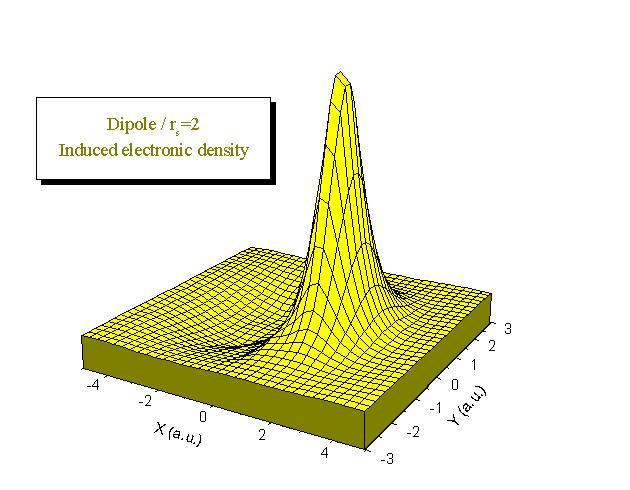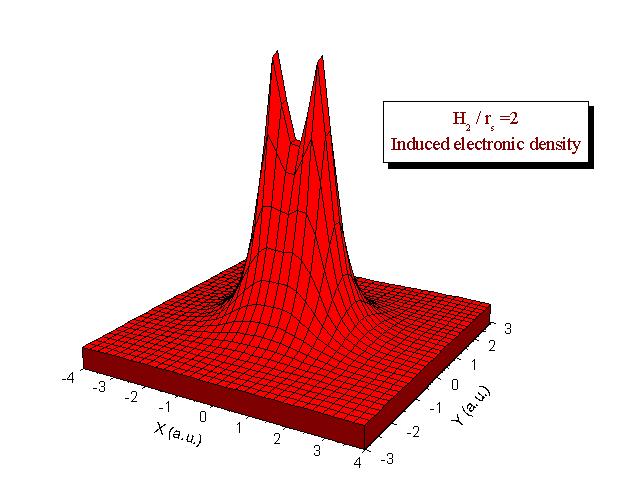
We use Density Functional Theory to calculate the electronic density induced by a diatomic molecule in a free electron gas as well as the embedding energy. Calculations may be performed for any dimer (see examples below:
H 2 , LiH and a dipole (Z= ±1)). We study the dependence of the results on parameters such as the internuclear distance or the mean electronic density of the medium. We show that the response of the medium is sensitive to the presence of an electric dipole moment in the isolated dimer. The electron gas either screens the interaction between the two centers of the molecule (H2) or favours the transfer of electronic charge between them (LiH and dipole). We also calculate the contribution of the electron-hole pairs excitations to the energy loss of a molecule when the latter is moving inside an electron gas. Our results show to be very useful to understand the adsorption mechanisms of molecules on metal surfaces.