Sensors based on NV centers in diamond
Design and characterization of sensors based on NV centers in diamond.
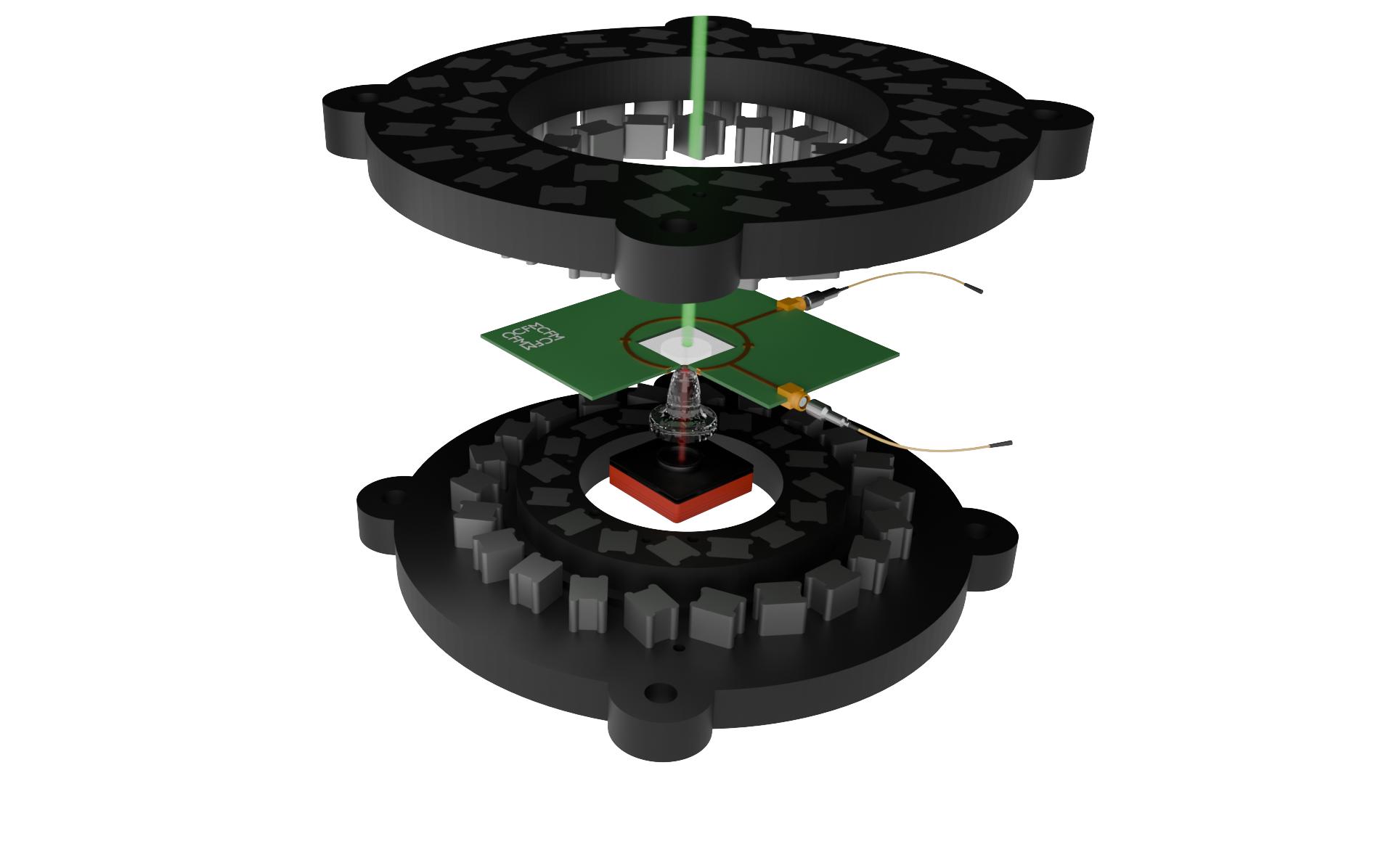
Nitrogen-vacancy (NV) centres are point-defects in diamond. They have exceptional photo-stability, controllable electronic spin state with long coherence times, and sensitivity to magnetic and electric fields, temperature, and pressure. These properties, which hold even at room temperature, and along with the accessible nuclear spin of the nitrogen, have made NV centres a popular candidate in quantum information and computing for single-photon generation and as spin-qubits, as well as various quantum sensing applications.
At the Quantum Nanophotonics Laboratory, we specialise in the exploration of novel quantum control and sensing methods with NV centres as well as in the development of portable and practical instruments. We currently have two platforms for bulk diamond chips with variable applied magnetic fields – one employing Helmholtz coils and another using moveable permanent magnet rings. Development of such platforms entails the integration of optics and electronics, and the design of versatile microwave antennas suited for the geometry of the application and that can precisely deliver the field parameters required. Beyond sensing in bulk diamond, we are also working on the control of single (or few localised) NVs for sensing at the nano- and micro-scales using a confocal microscope, and a fibre-based probe system.
Keywords: NV centres, quantum sensing, quantum control, magnetic fields, electric fields, spin, qubits.