Spectroscopy at atomic scale group
Electronic and magnetic properties
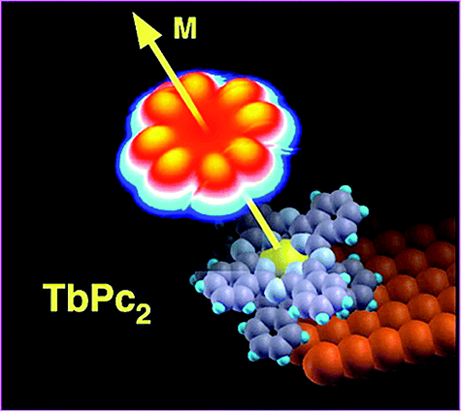

The emerging electronic and magnetic properties of interface depend on the nature of the coupled materials, on details of the atomistic structure of the interface and on the strength of their coupling. Adsorption and chemical bonding between organic molecules and between molecules and metal surface can result in a significant charge-transfer with a consequent shift and hybridization of the electronic orbitals. The nature and spatial localization of the electronic orbitals involved in the charge transfer process reflects the chemical structure of the molecule and its adsorption geometry. The degree of charge reorganization at the interface can be accessed by measuring the local density of states and the variation of the surface potential caused by induced dipoles at the interface (article). The knowledge of the charge localization is an important issue for the electron conductance and reactivity of metal organic interfaces.
The interface geometry plays a fundamental role in the electronic properties also in inorganic layers with a weak coupling-strenght to the supporting substrate. Moiré patterns characteristic of two dimensional layers with incommensurable lattice constant to the supporting layer show a spontaneous texturization of the electronic properties. This periodic modulation of the density of states reflect the variable atomistic registry at the interface. The opening of an energy gap of ∼0.5 eV at the Fermi level in an otherwise metallic layer, the patterning of the character of the hybridized Gd-d states and the shift of the center of mass of the Gd 4f multiplet are consequence of the different coupling geometry across the interface (article). Additionally, the electronic band structure of a weakly coupled layer can be tuned by a temperature controlled strain of the intra-layer atomic distance. The density of states has been observed to shift linearly in the range of 1–7%, leading to the formation of lateral hetero-structure (article).
The magnetic properties can be accessed through the characterization of the electronic properties. Our recent results shows that the Curie temperature of two dimensional alloys, namely the GdAu2 and the GdAg2, measured with space integrating techniques, is observed to scale with the density of state at the Fermi level. Thus, the Ag alloy shows a higher Curie temperature. (article). However, the magnetic anisotropy of the two probed Gd alloys are predicted to be space dependent according to the texturization of the electronic properties (article).
At molecular level, we have demonstrated that single-molecular-magnets molecules preserves their properties even upon adsorption on copper surfaces (article). The Kondo effect can also be monitored to determine the effect of adsorption geometry. Specifically, we have monitored the Kondo temperature of single Co adatoms supporthed on Cu(111) surface as a function of the proximity to a metal contact (article).
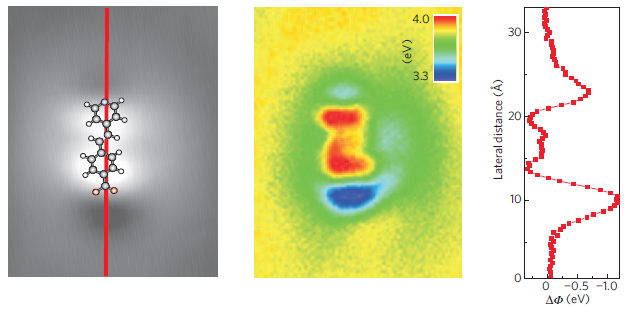
Potential barrier across a molecule-metal contact.
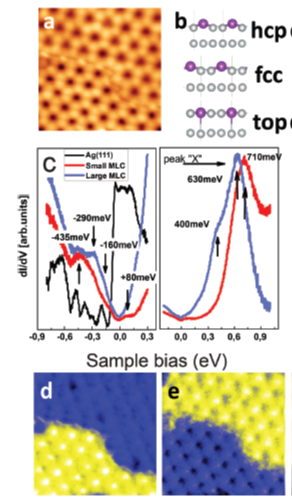
Structure and electronic properties of two domains of GdAg2/Ag(111) showing different lattice constant strain.
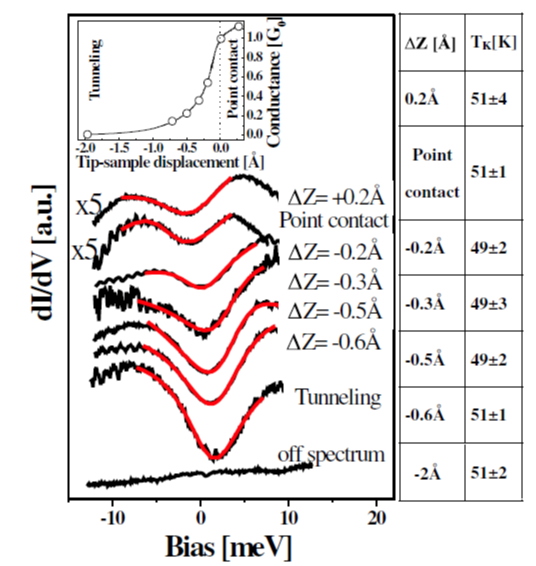
Conductance and dI=dV spectra for isolated Co atoms on a Cu(111) surface achieved at different tip-substrate distances from tunneling to the point contact.
Alexander Correa, Matteo Farnesi Camellone, Ana Barragan, Abhishek Kumar, Cinzia Cepek, Maddalena Pedio, Stefano Fabris and Lucia Vitali
Nanoscale 2017,9, 17342-17348
article
A. Correa, B. Xu, M.J. Verstrate L. Vitali
Nanoscale 8, 19148 (2016)
article
M. Ormaza, L. Fernandez, M. Ilyn, A. Magana, B. Xu, M. J. Verstraete, M. Gastaldo, M. A. Valbuena, P. Gargiani, A. Mugarza, A. Ayuela, L.Vitali, M. Blanco-Rey, F. Schiller, and J. E. Ortega
Nano Letters 16, 4230 (2016)
article
L. Vitali, P. Wahl, R. Ohmann, J. Bork, Y. Zhang, L. Diekhoener, and K. Kern
Physica Status Solidi B250, 2437- 2444 (2013)
article
R.Ohmann, G.Levita, L.Vitali, A.De Vita, K.Kern
ACS Nano 5, 1360-1365 (2011) .
article
S. Stepanow, J. Honolka, P. Gambardella, L. Vitali, N. Abdurakhmanova, T. C. Tseng, S. Rauschenbach, S. L. Tait, V. Sessi, S. Klyatskaya, M. Ruben, K. Kern
Journal of the American Chemical Society 132, 11900-11901 (2010).
article
R. Ohmann, L. Vitali, K. Kern.
Nano Letters 10, 2995-3000 (2010)
article
L. Vitali, G. Levita, R. Ohmann, A. Comisso, A. De Vita, K. Kern
Nature Materials 9, 320-323 (2010)
article
L.Vitali, R.Ohmann, S.Stepanow, P.Gambardella K.Tao, R.Huang, V.S.Stepanyuk, P.Bruno, K.Kern
Physical Review Letters 101, 216802 (2008)
L.Vitali, S.Fabris, A.Mosca Conte, S.Brink, M.Ruben, S.Baroni, K.Kern
Nano Letters 8, 3364- 3368 (2008)
article
L.Vitali, C.Riedl, R.Ohmann, I.Brihuega, U.Starke, K.Kern
Surface Science 602, L127-L130 (2008)
article
P.Wahl, L.Diekhoener, G.Wittich, L.Vitali, M.A.Schneider, K.Kern
Physical Review Letters 95, 166601 (2005)
article